Nano Composites in the Polyethylene Industry
-
Introduction
The polyethylene industry has experienced significant advancements in recent years, largely driven by the integration of nanotechnology and the development of nano composites. Nano composites are materials that combine nanoscale particles or fibers with a polyethylene matrix, offering a wide range of improved properties and functionalities. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of nano composites in the polyethylene industry, covering their composition, manufacturing techniques, properties, applications, and future directions.
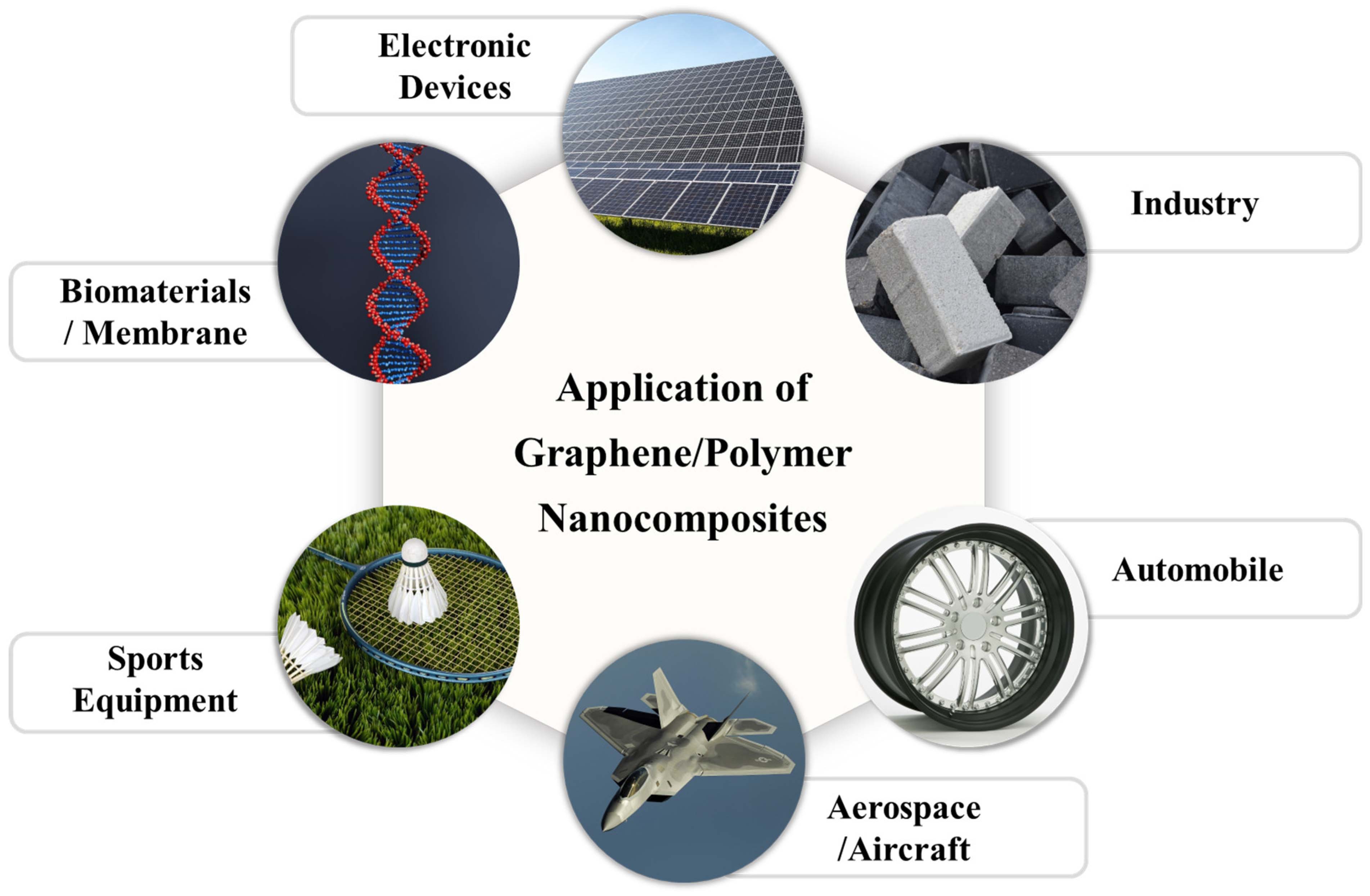
II. Fundamentals of Nano Composites
A. Composition of Nano Composites in the Polyethylene Industry
-
Nano Fillers: Types and Properties Nano composites incorporate various types of nano fillers, including carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene, clay nanoparticles, metal oxides, and nanocellulose. Each type of filler brings unique properties and characteristics to the resulting polyethylene nano composite.
-
Polyethylene Matrix: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
Polyethylene, in the form of HDPE or LDPE, serves as the matrix material in nano composites. HDPE and LDPE have different molecular structures, leading to distinct properties and suitability for different applications.
B. Manufacturing Techniques for Polyethylene Nano Composites
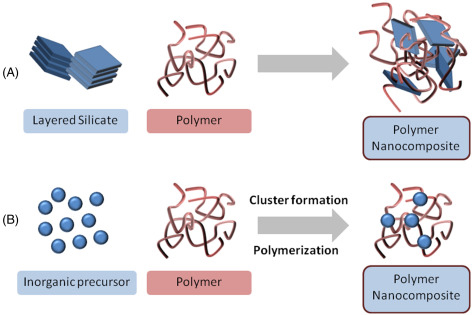
-
Melt Blending
Melt blending is a widely used technique in which the nano fillers are mixed with the polyethylene matrix by heating and melting the components. This process offers advantages such as simplicity, scalability, and compatibility with existing polymer processing equipment. However, achieving uniform dispersion of nano fillers in the matrix can be challenging.
-
In Situ Polymerization
In situ polymerization involves the synthesis of the polyethylene matrix and the incorporation of nano fillers simultaneously. This technique offers better control over the dispersion and interaction between the fillers and the matrix. It is particularly suitable for producing nano composites with tailored properties.
-
Solution Mixing
Solution mixing involves dissolving the polyethylene and the nano fillers in a solvent, followed by the removal of the solvent to obtain the nano composite material. This technique allows for better dispersion of nano fillers and control over the composite's properties. However, it may be limited to specific types of nano fillers and solvent systems.
-
Electrospinning
Electrospinning is a technique that involves the application of an electric field to create polymer fibers with nanoscale diameters. By incorporating polyethylene and nano fillers into the electrospinning process, it is possible to produce polyethylene nano composites in the form of nanofibers. This technique offers unique opportunities for applications requiring high surface area and mechanical strength.
III. Properties and Advantages of Polyethylene Nano Composites
A. Mechanical Properties Enhancement
-
Increased Stiffness
The addition of nano fillers to polyethylene enhances its stiffness, resulting in improved structural integrity and resistance to deformation. The type, size, and concentration of the fillers play a crucial role in determining the stiffness improvement.
-
Improved Strength and Toughness
Nano composites exhibit improved strength and toughness compared to pure polyethylene. The presence of nano fillers reinforces the polymer matrix, leading to enhanced resistance to fracture and impact.
-
Enhanced Abrasion Resistance
Polyethylene nano composites show improved resistance to abrasion, making them suitable for applications requiring high wear resistance, such as automotive components and industrial machinery parts.
B. Thermal Stability Improvement
-
Reduced Thermal Expansion Coefficient
Nano composites can mitigate the thermal expansion of polyethylene, making them more dimensionally stable across a range of temperatures. This property is crucial for applications exposed to thermal cycling and fluctuations.
-
Enhanced Heat Resistance
The inclusion of nano fillers in polyethylene enhances its heat resistance, allowing it to withstand higher temperatures without significant degradation. This property is advantageous in applications where exposure to heat is expected, such as automotive engine components and electrical insulation.
C. Barrier Properties Enhancement
-
Gas Barrier Properties
Polyethylene nano composites can exhibit improved gas barrier properties, reducing the permeation of gases through the material. This property is particularly valuable in packaging applications, where it helps prolong the shelf life of perishable goods and maintains the quality of sensitive products.
-
Moisture Barrier Properties
Nano composites can enhance the moisture barrier properties of polyethylene, reducing the ingress and egress of water vapor. This characteristic is crucial in applications where moisture resistance is essential, such as food packaging, electronics, and construction materials.
D. Electrical Conductivity and EMI Shielding
-
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) and Graphene as Conductive Fillers
CNTs and graphene, when incorporated into polyethylene, can impart electrical conductivity to the composite material. This property opens up opportunities for applications in electronic packaging, conductive coatings, and electrical interconnects.
-
Applications in Electronic Packaging and EMI Shielding
Polyethylene nano composites with conductive fillers can provide effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. This capability is valuable in electronic devices and systems where electromagnetic compatibility is crucial.
E. Surface Modification and Functionalization
-
Antimicrobial Activity
Nano composites can be modified to exhibit antimicrobial properties, making them suitable for applications in healthcare, food processing, and packaging. The controlled release of antimicrobial agents from the composite material helps inhibit the growth of microorganisms.
-
Flame Retardancy
The addition of flame retardant nano fillers to polyethylene improves its resistance to ignition and reduces the spread of flames. This property is critical in industries where fire safety is paramount, such as construction, transportation, and electronics.
-
Self-Healing Capabilities
Some polyethylene nano composites have the ability to self-heal when subjected to damage or mechanical stress. This property enables the material to repair itself, extending its lifespan and improving durability.
-
UV Resistance
Nano composites can enhance the UV resistance of polyethylene, protecting it from degradation caused by exposure to sunlight. This characteristic is valuable in outdoor applications, such as construction materials, automotive components, and outdoor furniture.
IV. Applications of Polyethylene Nano Composites
A. Packaging Industry
-
Food Packaging
Polyethylene nano composites offer improved barrier properties, extending the shelf life of food products and reducing food waste. The enhanced mechanical strength and resistance to puncture and tear make them ideal for flexible food packaging.
-
Flexible Films
Nano composite-based flexible films provide enhanced mechanical properties, gas barrier properties, and moisture resistance. These films find applications in various industries, including food packaging, medical packaging, and agricultural films.
-
Protective Coatings
Polyethylene nano composites can be used as protective coatings to enhance the corrosion resistance of metals, concrete, and other substrates. They offer improved adhesion, mechanical strength, and durability, extending the lifespan of coated surfaces.
B. Automotive Sector
-
Interior and Exterior Components
Polyethylene nano composites find applications in automotive interior and exterior components, such as bumpers, panels, and trims. They contribute to weight reduction, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced aesthetics, while maintaining durability and impact resistance.
-
Fuel Efficiency and Safety Improvements
The use of polyethylene nano composites in automotive components can contribute to improved fuel efficiency by reducing the weight of the vehicle. Additionally, the enhanced strength and impact resistance of the composites enhance passenger safety.
C. Construction Materials
-
Concrete Rein
forcement
Polyethylene nano composites can be used to reinforce concrete structures, enhancing their strength, durability, and resistance to cracking. These composites improve the performance of infrastructure components such as beams, columns, and bridge decks.
-
Lightweight Building Components
Nano composite-based polyethylene materials offer the advantage of lightweight construction components. They can be used in applications such as insulation materials, cladding panels, and roofing systems, contributing to energy efficiency and sustainability in the construction industry.
D. Biomedical Field
-
Implantable Devices
Polyethylene nano composites have potential applications in implantable medical devices due to their biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and surface modification capabilities. They can be used in orthopedic implants, dental implants, and tissue engineering scaffolds.
-
Drug Delivery Systems
Nano composites based on polyethylene can be utilized in drug delivery systems to enhance drug stability, control release rates, and target specific tissues or cells. These systems offer opportunities for personalized medicine and targeted therapies.
-
Tissue Engineering Scaffolds
Polyethylene nano composites can serve as scaffolds for tissue engineering, providing a biocompatible and mechanically supportive structure for tissue regeneration. They offer opportunities for the development of engineered tissues and organs.
-
Wound Dressings
Nano composite-based wound dressings can provide advanced functionalities such as antimicrobial activity, moisture management, and controlled drug release. These dressings promote wound healing and prevent infection.
V. Future Directions and Challenges
A. Continued Research and Development
-
Optimizing Manufacturing Processes
Ongoing research aims to optimize the manufacturing processes of polyethylene nano composites, improving dispersion, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Innovations in melt blending, in situ polymerization, solution mixing, and electrospinning are being explored.
-
Improving Dispersion of Nano Fillers
Efforts are focused on achieving better dispersion and alignment of nano fillers within the polyethylene matrix. Techniques such as surface functionalization, compatibilizers, and processing parameters optimization are being investigated.
-
Exploring Novel Polymer-Additive Combinations
Researchers are exploring new combinations of polyethylene and nano fillers to tailor the properties of the resulting composites. This includes the development of hybrid materials and the incorporation of multi-functional additives.
B. Regulatory Considerations
-
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of polyethylene nano composites throughout their life cycle is an area of concern. Research is being conducted to assess their potential impact on ecosystems, as well as to develop sustainable disposal and recycling strategies.
-
Health and Safety Considerations
As with any new materials, the potential health risks associated with polyethylene nano composites need to be thoroughly evaluated. Studies are being conducted to understand the behavior of nanoparticles in the body and establish safety guidelines for their use.
-
Recycling Feasibility
Developing efficient and cost-effective recycling methods for polyethylene nano composites is a significant challenge. Research efforts are focused on finding sustainable approaches to recover and reuse these materials, promoting a circular economy.
C. Scale-Up and Cost Considerations
-
Efficient Large-Scale Production
Scaling up the production of polyethylene nano composites while maintaining quality and consistency is a key challenge. Optimization of manufacturing processes, equipment selection, and quality control methods are being explored.
-
Cost-Effective Sourcing of Nano Fillers
The cost of nano fillers can significantly impact the overall cost of polyethylene nano composites. Research aims to identify cost-effective sources, develop scalable synthesis methods, and explore the use of alternative fillers with comparable properties.
VI. Conclusion
Polyethylene nano composites have emerged as a promising class of materials, offering enhanced properties and functionalities compared to traditional polyethylene. These composites have diverse applications in packaging, automotive, construction, and biomedical fields. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on optimizing manufacturing processes, improving dispersion, addressing regulatory considerations, and ensuring cost-effectiveness. By overcoming these challenges, the future of polyethylene nano composites holds tremendous potential, paving the way for sustainable, efficient, and technologically advanced applications in various industries.
Read More:
Composite Manhole Cover
Application of polyethylene fittings
Pars Ethylene Kish Product Application
Application of polyethylene pipe in mine
Polyethylene fittings
Polyethylene manhole